
This year has been particularly turbulent for ESG reporting. Ongoing regulatory uncertainty in Europe—highlighted by the still-unresolved CSRD omnibus—has left many organizations unsure about what to disclose, when, and in what format. At the same time, AI ESG reporting is gaining momentum, offering companies an efficient way to manage the increasing volume and pace of disclosures. As a result, more professionals are seeking to strengthen their sustainability intelligence through resources like this introduction to AI in sustainability and ESG practices to stay aligned with evolving business needs.
Currently, corporate teams face challenges and confusion for two main reasons. Firstly, they have a difficult time fully grasping the complexity of existing ESG frameworks. Then, it is the pressure of investors who demand clear and justifiable data, setting the level of tangible commitment to sustainable and ethical operations.
A company’s strong ESG performance translates into actual operations that fully encompass KPIs, initiatives, and strategies. When disclosures are valid, they make a real impact, inspiring trust in stakeholders and investors.
Standards like GRI, SASB and ESRS aim for structured data and transparency during disclosures. Well-written narratives no longer convince. But due to limited resources, loads of data, and the juggling between changing taxonomies, organizations view this process as mainly an unpleasant burden. In this response, more organizations turn to AI tools, as they consider them necessary to support them in this process.
In this piece, we discuss the powering role of Artificial Intelligence in ESG reporting. What are the pros and cons of using it, and how can real-world case studies that have engaged with AI ESG reporting tools show the way to more companies?
According to research, 63% of companies already use or think of using AI to collect their ESG data, analyze them, and report. AI in ESG and Sustainability is in a growing orbit; it is currently valued at $1.24 billion and is expected to reach $14.87 billion by 2034. This trend shows that more organizations acknowledge that AI ESG Reporting has dynamic potential in facilitating the process. However, there are also limitations along the way to be considered.
More companies are welcoming digital transformation to automate and improve their operations. Accordingly, in ESG reporting, AI can support the handling of a large workflow by organizing extensive amounts of data that need to be efficiently structured.
Classification and Scalability: Bringing together ESG-relevant content scattered across different teams and departments is a demanding task, so starting with the important step of recognizing all things ESG-related and entering them in databases increases scalability and saves time, especially around reporting cycles.
Optimization and Insights: AI algorithms used in NLP and machine learning tools process vast amounts of unprocessed data into ESG insights that inform decisions. These tools can extract millions of texts, providing relevant sustainability information, while they also suggest proper visualization, optimizing ESG disclosures.
Risks Monitoring in Real-Time: By connecting IoT devices, AI can create live dashboards, access live news feeds, and analyze data and indicators that are related to emissions trends and resource use as well as compliance metrics. Teams can detect any irregularities, particularly in complex supply chains where manual monitoring proves challenging. These systems, also enabling forecasts, allow companies to quickly adapt to the changing environmental and social challenges.
Framework Interoperability and compliance: In the context of evolving ESG standards, AI ESG Reporting systems support the simultaneous mapping and development of ESG data standards and the interoperability of frameworks so that information exchange is coherent across different regions. That helps companies manage alignment while strengthening the process toward compliance, avoiding double reporting.
Cost Allocation during ESG Compliance: Organizations that invest in AI technology recognize how efficient it is to have smarter management over financial allocation during their ESG compliance operations. Automation in data processing significantly eliminates manual workload and operational risks, which leaves room for fewer errors that are costly for companies. AI allows teams to pay attention to tasks that require a more strategic approach during compliance operations.
Every coin has two sides, and so the sole use of AI technology is not a panacea in ESG reporting. It projects limitations that sustainability teams should not ignore.
Qualitative database and availability: The ESG data field is mostly characterized by diversity in completion and consistency, especially in some industries or regions. AI algorithms can misunderstand gaps in data analysis and standardization, failing to be objective, therefore compromising the validity and quality of ESG databases.
Data privacy and responsibility: ESG data can include sensitive information, as they concern not only stakeholders (for example, suppliers and employees) but also environmental and social aspects. AI ESG reporting must be underlined by responsibility and comply with data privacy and protection rules; otherwise, it can raise questions over ethics that undermine sustainability goals.
“Black box” issue and Ethics: Even the latest editions of machine learning models can address the “black box” challenge, which means they can draw conclusions without providing clear reasoning. In AI ESG reporting, there is always the possibility of distorting data by failing to make proper risk assessments. The issue reminds us that human evaluation can be more easily justifiable, as it acknowledges ethics and bias where AI models can’t.
ESG Issues dynamics and liability: ESG standards and frameworks are continuously evolving, as are global social and environmental matters. AI ESG reporting tools and software must be affordable and aligned with global changes.
Human Skills and AI literacy: As AI technology is further linked to ESG reporting, professionals who are engaged with these processes must learn how to combine their sustainability backgrounds with AI literacy to close the gap in the unskilled workforce in this field. Training in sustainability intelligence, which also fosters an understanding of AI ESG reporting, enables professionals to take the lead.
Despite the challenges presented, there are companies that have not hesitated to embrace AI technology in their ESG reporting. They view AI ESG reporting tools as a strategic ally to their disclosure journey, one that helps them to streamline complex data with improved analysis and unlock valuable opportunities that drive growth.
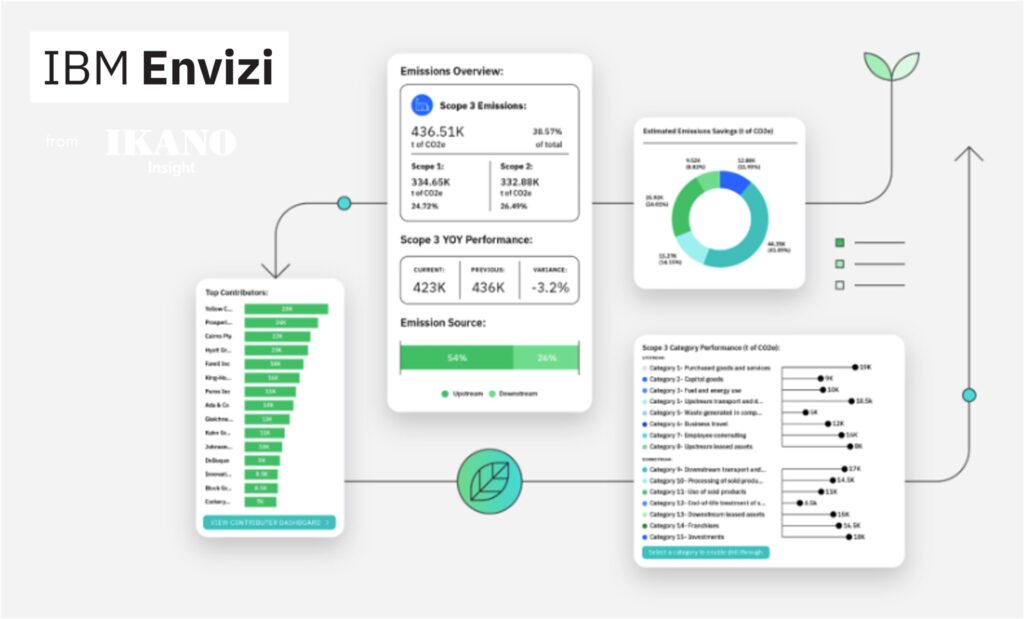
source: Ikano Insight
Ikano Insight, a UK based company and part of the Ikano Group, focuses on retail analytics, and it is a leader in putting sustainability at the front of its operations. Its priority is to offer solutions that improve people’s lives by playing its significant part in creating a sustainable future for everyone.
Ikano Group aims to publish its first CSRD reporting and the ESRS standards in 2026. However, due to the complexity of ESG data and the fact that its operations span around 6 diverse businesses spread across 3 continents, Ikano had a challenging effort to make in terms of collecting, analyzing, and reporting.
To stay committed to its sustainability journey and maintain its brand reputation and consumer trust, Ikano understood that it has to successfully comply with the CSRD requirements. In this context, Ikano recognized that harnessing the most of technology is a straightforward approach for addressing their needs. Thereby, they came up with an ESG reporting solution that ensures transparency while supporting work towards the diversity of the Group’s sustainability targets.
Ikano Insight, which is also an IBM business partner, provided the answer by choosing the Envizi software platform. The IBM Envizi ESG suite is using machine learning and other AI features to enable automated processes when capturing and analyzing ESG data. Its technology supports companies in measuring emissions with accuracy and detecting risks and opportunities to improve sustainability performance.
By utilizing Envizi’s AI possibilities, Ikano Group integrated all its ESG KPIs into operations while it completed an ESG data common map, enabling all companies to use this workflow and respond according to the ESRS framework. The AI-powered Evizi platform, implemented by Ikano Insight, had a dual impact. Not only did it simplify the data capture and reporting by saving hundreds of hours and money in resources, but it also authorized individual companies to access it and initiate pivotal actions.
One of the constraints of AI ESG reporting is the adequate knowledge required to use such platforms. Ikano made sure to train all administrators and users involved to effectively engage with the platform to bring about a seamless result.

source: Natera
In the United States, Natera, Inc., a clinical genetic testing company that operates in the Biotech & Pharma industry, specializes in DNA testing technology that focuses on women’s health and oncology. Natera’s priority lies in its deep care not only for the people but also for the planet. Therefore, it constantly aims for a business strategy that reflects its focus on sustainability goals.
Regulations like California’s SB 253 and the SEC Climate Disclosure Rule demand a clear and valid GHG emissions report. Stakeholders kept raising questions on the reliability of carbon footprint calculations, causing Natera concerns over confidence in audit-ready data. According to their statements, previous years were not that strong in carbon accounting, as there was limited visibility of data. This situation created a sense of insecurity when they had to publish their numbers on their ESG reports.
To enhance confidence and ensure that their GHG emissions data were reliable, they decided they had to scale up their data management with a more technological approach. Persefoni is a climate management & accounting platform that helps professionals comprehend GHG protocol, bringing it into line with their own business measures. The platform is designed with the utilization of sophisticated AI technology in mind, including GPT models that ensure data are valid and precise.
Natera’s ESG team can collect information easier from the different departments and streamline data and calculation, while their communication with external stakeholders has been smoother. The facilitation through AI ESG reporting has increased Natera’s confidence and has left room for strategic actions as they continue to refine and improve emissions calculations, especially with Scope 1 and 2.
More companies are integrating AI into ESG reporting as they witness in action how it helps them in tracking measurable data and making smarter improvements. AI systems work as a necessary shortcut to gaining sustainability performance insights that can save substantial time and money, especially when companies compile reports. Additionally, the option of detecting risks in a timely manner lets organizations make efficient decisions and adapt to environmental and social changes. However, despite the significant optimization and scalability that AI ESG Reporting tools can bring to sustainability teams’ table, the field is still progressing. That means there is significant experimentation and learning taking place, especially when collecting qualitative data. For example, it is not possible to abstractly access sensitive and private information without complying with proper regulations.
Human evaluation in AI ESG reporting remains indispensable during disclosure periods, as professionals bring an ethical perspective that technology alone cannot replicate. Organizations must exercise caution when adopting AI-driven ESG reporting innovations, carefully weighing the benefits and potential risks. Developing AI expertise through a sustainability lens is vital. For executives committed to ESG, investing in focused sustainability intelligence training is a powerful way to ensure their companies maintain long-term, consistent practices across growth and geographic expansion. To strengthen this understanding, leaders can also explore insights on national AI strategies and what they must know to align innovation with responsible governance.
