

Strong ESG credentials drive down business costs by 5 to 10 percent, which is a major benefit for organizations embracing sustainable practices. Sustainable procurement integrates environmental, social, and governance considerations into purchasing decisions, seeking to achieve the lowest environmental impact alongside the most positive social outcomes. This approach stands at the forefront of modern business strategy, balancing ecological responsibility with social accountability.
The adoption of sustainable procurement practices transcends mere cost reduction, emerging as a powerful catalyst for organizational differentiation in the marketplace. Companies implementing strategic sustainable procurement experience a measurable 15–30% increase in brand value. These practices reduce procurement costs by 9-16%, enhancing financial performance while harmonizing with the triple bottom line concept—People, Profit, and Planet. Public spending constitutes approximately 12% of GDP in OECD countries, underscoring the substantial purchasing power available to steer markets toward sustainability.
This guide illuminates how developing an effective sustainable procurement policy bolsters your organization’s long-term objectives. The following sections present practical examples of sustainable procurement in action, outline the essential components of a robust sustainable procurement strategy, and explain why green procurement has evolved from an optional approach to a business imperative for 2025.
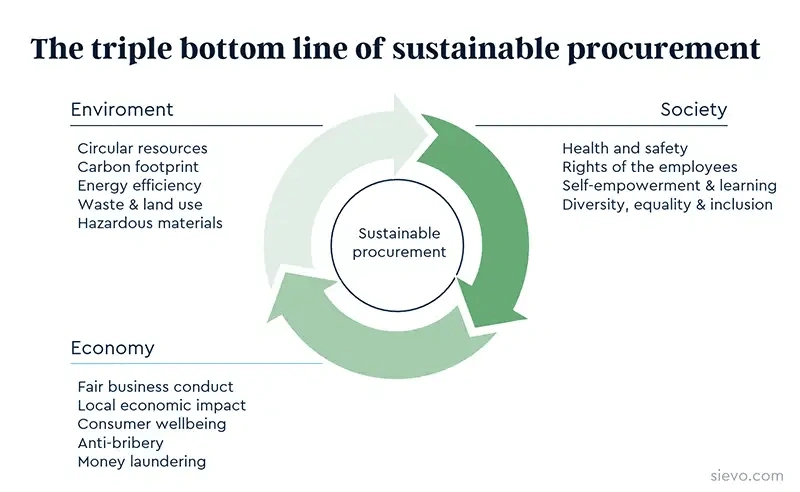
Image Source: Sievo
Sustainable procurement has undergone a remarkable evolution, transitioning from a mere compliance exercise to a strategic imperative for forward-thinking organizations. This process integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into procurement decisions and ensures that stakeholder requirements are satisfied. The fundamental aim centers on achieving minimal environmental impact while simultaneously generating the most beneficial social outcomes.
Distinguishing Green from Sustainable Procurement
Although green procurement and sustainable procurement are often used interchangeably, they represent distinct approaches to responsible purchasing. Green procurement narrows its focus exclusively to environmental considerations, such as the acquisition of recyclable products and energy-efficient systems. Sustainable procurement, by contrast, adopts a more holistic perspective, encompassing social and economic dimensions alongside environmental concerns.
The Triple Bottom Line (TBL) framework forms the cornerstone of sustainable procurement, extending beyond conventional financial reporting to embrace
Key Shifts Defining Sustainable Procurement in 2025 and beyond
The landscape of sustainable procurement for 2025 exhibits several pivotal transformations. Organizations are moving from merely setting ambitious ESG targets to concrete implementation supported by sophisticated tools and methodologies. This shift has prompted businesses to incorporate specialized positions, such as ‘Sustainable Purchasing Manager’ into their organizational frameworks.
The demand for information accuracy has intensified significantly. Organizations now seek tangible evidence supporting sustainability claims rather than accepting unverified statements. This heightened emphasis on data quality enables companies to monitor trends proactively and develop more profound insights into supply chain ESG risk patterns.
The strengthening of supplier relationships emerges as another crucial trend for 2025. While many buyer-supplier interactions have grown increasingly transactional in nature, this approach undermines the stability and trust essential for sustainable partnerships. Consequently, organizations are cultivating deeper collaborative relationships and implementing digital tools that empower suppliers, and foster shared innovation and ethical practices throughout the supply chain.
Sustainable procurement thus stands as a powerful mechanism for positive transformation, delivering substantial benefits across organizational, societal, and environmental domains.
The business case for sustainable procurement extends far beyond environmental stewardship, delivering tangible advantages across multiple organizational dimensions. Companies that embrace these practices witness a substantial 15–30% increase in brand value, fostering deeper customer loyalty and attracting a growing segment of environmentally conscious consumers.
Financial returns from sustainable procurement prove remarkably compelling. The World Economic Forum’s research reveals these practices can reduce procurement costs by 9-16%, achieved primarily through decreased energy consumption, reduced resource usage, and lowered compliance expenses. McKinsey’s analysis further confirms this trend, noting that robust ESG credentials drive down business costs by 5-10% as companies enhance operational efficiency and minimize waste generation.
The strategic value of sustainable procurement manifests powerfully in risk mitigation capabilities. Organizations implementing these approaches effectively shield themselves against supply scarcity and evolving social, economic, and environmental conditions. This proactive stance strengthens supply chain resilience by diversifying sourcing strategies and cultivating more robust supplier relationships.
The investment community increasingly recognizes sustainability’s importance, with 75% of UK investors now evaluating a company’s ESG risk exposure during investment screening. Most significantly, 79% of these investors support sustainability expenditures even when such investments temporarily reduce short-term profitability.
Regulatory preparedness emerges as another crucial benefit. As sustainability regulations grow increasingly stringent worldwide, organizations with established sustainable practices position themselves advantageously to meet emerging requirements without operational disruption.
The talent acquisition dimension proves equally significant, with 33% of businesses intensifying their sustainability focus specifically to address challenges in attracting, motivating, and retaining skilled personnel. In today’s competitive employment landscape, a robust sustainability strategy offers a genuine advantage in securing top talent.
Sustainable procurement thus creates meaningful differentiation that resonates across all stakeholder groups—from customers and investors to employees and regulatory bodies—establishing its position as an indispensable business strategy for 2025 and beyond.
The Global Reporting Initiative’s push for sustainability in business practices finds tangible expression through diverse procurement initiatives across multiple sectors. These real-world applications showcase how organizations translate theoretical sustainability commitments into actionable purchasing strategies, demonstrating the practical implementation of ESG principles throughout global supply chains.
IT hardware procurement represents a significant area where sustainability considerations have gained prominence. Microsoft’s sustainability reporting reveals that 77% of their emissions stem from scope 3 sources—the carbon footprints of their suppliers and consumers. Forward-thinking organizations concentrate their efforts on three essential dimensions:
The cocoa sourcing sector illustrates how companies address complex sustainability challenges in agricultural supply chains. Fazer has tackled unsustainable farming practices by emphasizing supplier development and selecting partners who adhere to their Supplier Code of Conduct. Despite these efforts, 80% of the 5 million cocoa farmers worldwide remain outside any certification program. Nestlé’s approach includes Child Labor Monitoring and Remediation Systems that identify at-risk children and provide remediation through educational infrastructure and access.
Office supplies procurement has undergone substantial transformation as organizations shift toward recycled and reusable materials. This evolution encompasses refillable pens, recycled chipboard binders, and alternatives to single-use products. Beyond merely selecting eco-friendly products, companies are implementing centralized supply management and proper material-specific disposal systems to maximize sustainability benefits.
Paper procurement demonstrates how government entities leverage their purchasing power for environmental impact. The Office of Government Procurement established a framework for 100% recycled office paper valued at approximately €6 million annually. This transition to recycled paper conserves an estimated 8.6 million kg of virgin wood—equivalent to approximately 6,000 spruce trees.
The single-use plastics category showcases innovative approaches to reducing environmental footprints in consumer-facing industries. Finnair exemplifies this trend through its renewal of onboard amenities, replacing plastic toothbrushes with bioplastic containing cornstarch and substituting plastic wrappings with wax paper. These changes reduced the airline’s plastic waste by nearly 4,500 kilograms annually.
Sustainable procurement stands at the intersection of business success and global responsibility. The evidence confirms how this approach yields measurable advantages across multiple dimensions. Cost reductions of 5-10% paired with brand value increases of 15-30% present compelling financial justifications for implementation. These figures underscore the tangible benefits that extend beyond environmental stewardship to directly impact organizational performance.
Your organization gains significant risk mitigation capabilities through the cultivation of stronger supplier relationships and decreased resource dependencies. These advantages transcend immediate financial returns, establishing enduring competitive differentiation in an increasingly sustainability-conscious marketplace.
The evolution from theoretical sustainability targets to concrete implementation denotes a watershed moment for businesses in 2025 and beyond. Procurement teams must now prioritize verifiable sustainability data rather than vague assertions or claims. This emphasis on accountability ensures authentic progress toward environmental and social objectives while satisfying the heightened expectations of consumers and investors alike.
Real-world applications across diverse categories—IT hardware, cocoa sourcing, office supplies, paper procurement, and single-use plastics—illustrate how organizations successfully translate these principles into practice. Each category presents distinct opportunities to align purchasing decisions with core sustainability values, demonstrating the versatility of sustainable procurement approaches.
Sustainable procurement serves a strategic need rather than simply a trend. Businesses applying this strategy position themselves optimally for investor confidence, talent attraction, and regulatory compliance. Thus, the triple bottom line framework grows into a foundation for wise decision-making, honoring people, planet, and profit in equal proportion.
The decisions your organization makes today regarding procurement practices will shape both business resilience and environmental impact for years to come. The question becomes not whether your business can afford sustainable procurement, but rather whether it can afford to operate without it. This collective endeavor toward sustainable procurement practices stands as a testament to the business community’s commitment to fostering a more sustainable and equitable future.
