
Published research on climate change no longer stresses its gravity with simple skepticism. There are recorded facts about how climate change drives the most intensifying and frequent extremes on a global scale. The results are so evident that they underline how the planet’s map of environmental challenges should immediately change.
Heatwaves, floods, and wildfires have already become commonplace in today’s world. Unfortunately, even the most rapid cut of emissions cannot erase the near-term impacts.
AI climate resilience can be achieved by using state-of-the-art technology to limit the effects of climate change and show progress that is both impressive and promising.
Artificial Intelligence serves as a crucial tool for enhancing climate resilience. It identifies risks promptly and in detail and enables the transformation of vast amounts of data from sensors, satellites, and community inputs into actionable early warnings.
Forecasting disastrous weather events, optimizing water and waste, and developing evacuation plans are some of the areas that AI climate resilience projects apply to.
As more companies deploy AI in innovative projects, paired with professionals’ skilled knowledge, we bring together five groundbreaking AI climate resilience projects that will make a real impact in 2025 and beyond.
The global picture of floods is concerning since it is one of the deadliest hazards taking place. As the air becomes warmer, holding around 7% more moisture per °C, heavy downpours are a common phenomenon. Sea level is rising at a faster pace, causing coastal floods. The disasters have not only affected communities but have also had serious economic consequences, especially in regions such as Spain and Brazil, according to the recorded toll in 2024 by the World Meteorological Organization. Early warning and forecasting can support risk-informed planning.
Google’s Flood Forecasting System is leading in AI climate resilience solutions with innovative machine learning approaches.
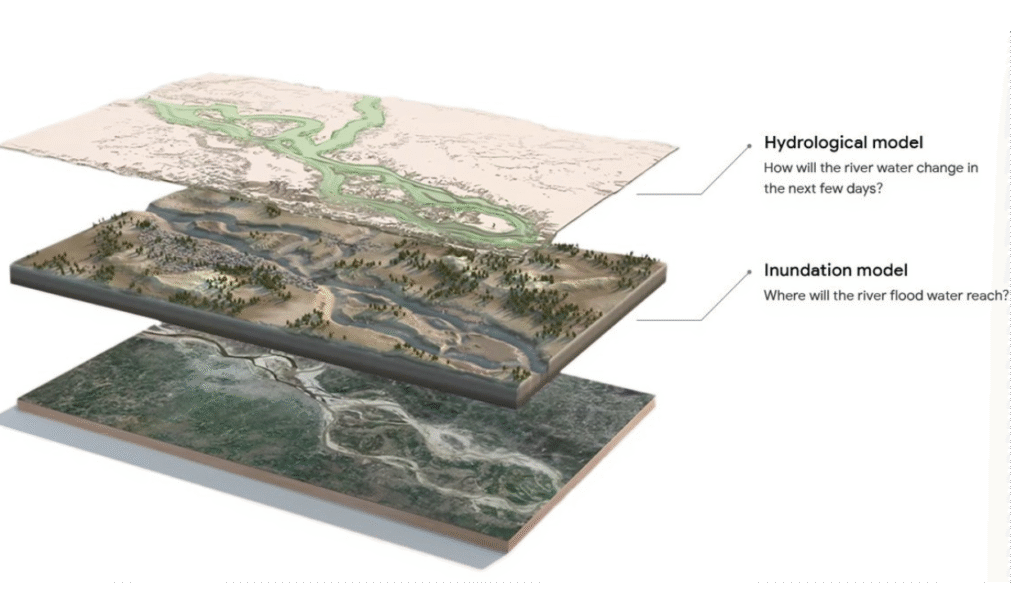
source: google
The flood-forecasting initiative was pilot-launched in 2018 in India’s Patna region, and it has expanded into one of the most accurate early-warning systems worldwide. It managed to replace traditional local data models with advanced AI technology to deliver accurate predictions, covering flood forecasting in more than 80 countries and protecting more than 500 million people. Where possible, Google Search, Google Maps, and Android notifications also provide these forecasts.
According to the system, there are two AI models combined. First, the hydrologic model predicts river flows using weather forecasts and satellite imagery. Then the inundation model simulates the way the water is likely to spread across floodplains, helping to identify which areas are likely at risk and what the water levels are.
Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) neural networks are behind the two models, according to which they read sequential data and can understand lasting patterns. By generating forecasts based on probability from historical data and current conditions, they use “virtual gauges” in areas where there are no physical tools to close coverage gaps.
In terms of climate resilience, this AI-powered technology has managed to significantly reduce deaths related to floods by up to 43%, while losses in the economy have been reduced by 35–50%. Early warning systems have helped communities by notifying them a week in advance, so they have preparation time to protect themselves and take evacuation measures. Even in areas where meteorological framing is not feasible, the system has improved forecast reliability, such as in Africa, largely matching the European standards.
Prior to the floods that took place in Brazil in May 2024, Google, in coordination with Brazil’s Geological Service, monitored over 200 new locations, and the concentrated data helped authorities and residents roll out effective crisis response strategies. These plans were used to predict and send supplies to the affected areas on time.
The project’s journey is not yet complete. There are challenges that must be addressed. The main obstacle is scarcity in data and the fact that there are streamflow gauges in only 1% of the world’s watersheds, limiting the monitoring potential. There is a correlation between economic development and data availability, with less developed countries providing insufficient hydrological data; therefore, they face higher flooding risks.
Next steps for Google are to intensify studies that relate to flood-type predictions such as flash floods and urban floods. Partnerships with initiatives such as the UN’s Early Warnings for All aim to inform about future climate hazards.
Earth’s variety of life, standing for biodiversity, is on a serious decline. The health, condition, and function of global biodiversity are under threat due to human activities, which are the main cause of this devastating loss. According to the World Health Organization, it is thought that extinction rates are 10-100 times higher than in the past.
Wildbook, developed by Wild Me, a nonprofit organization, offers cutting-edge AI powered solutions to monitor wildlife globally and contribute to its protection plans.

To fight extinction, it is important to collect valuable insights, and Wildbook manages to bring together wildlife research with the use of AI along with citizen science and computer analysis. Its ai-powered tools started with whale sharks, and now it has grown its platform to support hundreds of wildlife researchers tracking more than 188,000 individual animals worldwide. The tools help researchers implement their ecological methods for studying and counting species worldwide, effectively managing the large amounts of data provided by scientists.
The technology is based on computer vision machine learning. By scanning images with detection algorithms, the platform identifies animals and applies species labels from a vast database, significantly speeding up the work that researchers previously took an extensive amount of time to complete.
Using groundbreaking technologies in biodiversity monitoring has a notable impact on climate resilience. It provides the framework needed to not only receive early warnings prior to ecosystem changes but also to build data to measure and ultimately develop conservation strategies.
The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species™, which is the most comprehensive source of information on the extinction risk of animals and plants, utilizes Wildbook’s data for several species. Kenya Wildlife Service is also an example of utilizing Wildbook’s AI algorithms as the foundation of their endangered species management policy to identify massive information that would otherwise take months to carry out.
As with every tool that embraces technology, it presents some hurdles to overcome. In this case, data validation is the most common issue that ensures accurate species identification in crowdsourced images. Most people prefer intriguing locations over representative coverage. Additionally, Wild Me is still working with limited resources when supporting research, compared to the possibilities of other tech giants for AI talent.
Joining larger technological ecosystems is included in Wildbook’s growing strategic plans, with Microsoft’s AI for Earth program supporting the platform to give access to cloud computing resources that can improve scalability.
Wildfires have been perhaps one of the most disappointing negative results of climate change. The hotter and drier conditions create an ideal environment that fuels the initiation of fires, releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere and further speeding up warming and the circulation of intense fires (feedback loop). Millions of hectares of forests are burned by wildfires, a major factor in rising emissions, adding around 22% to global CO₂ emissions from fossil fuels.
Dryad Networks, a Berlin-Brandenburg environmental IoT startup, is committed to tackling the crisis with its innovative early detection system that recognizes fires before they are uncontrolled.
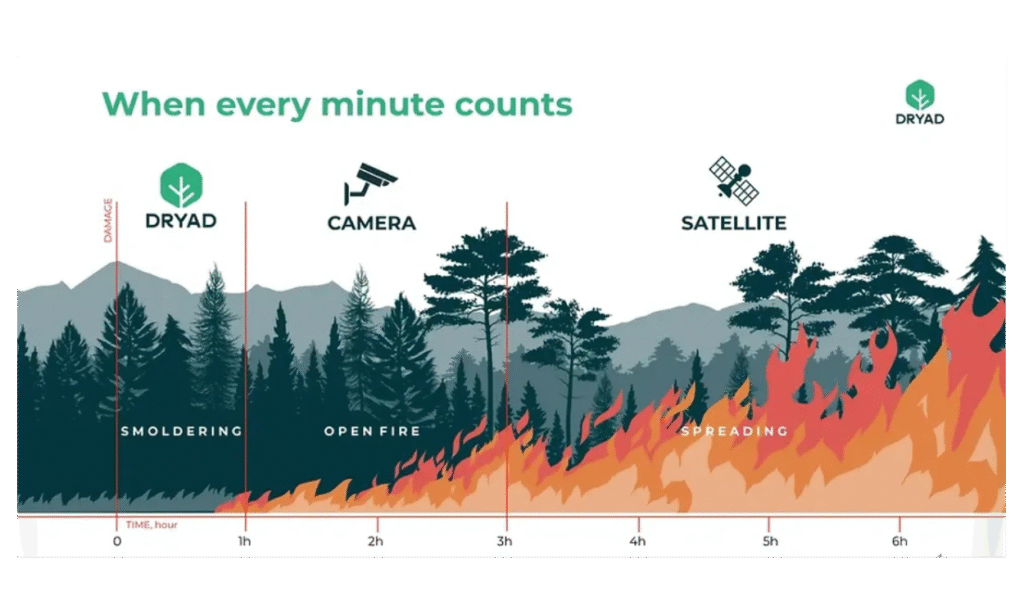
source: Dryad
Dryad’s main product, Silvanet, uses a large-scale IoT network that offers valuable insights and analytics and informs forest owners on how to watch, study, and protect vast remote forests. Dryad’s commitment is both inspiring and ambitious, as it intends to safeguard 2.8 million hectares of forest from wildfires by 2030.
The system runs on a network of solar-powered gas sensors attached to trees that can detect fires during their first flickering phase, often within minutes. Its wireless environmental sensor network uses LoRaWAN, and Its architecture, still in the patent process, can set up massive networks in places where there isn’t already coverage. Cloud-based big data solutions are used to analyze, monitor, and send alerts about data that is collected on the network.
Dryad’s technology comes as significantly impactful when discussing AI climate resilience. Its ability to spot flames before they break out—when cameras or satellites take hours or days to observe fires—has contributed to the reduction of carbon emissions while also protecting against wildfires and avoiding economic losses.
In Lebanon, an unauthorized fire was caught within half an hour, preventing what could have led to a disaster. Utility companies find this technology beneficial, as it provides an affordable solution to fires caused by power lines.
Even the most successful technological tools can engage with difficulties. Dryad, accordingly, faces the challenge of making gas-based fire detection both accurate and reliable, especially when they have to separate the actual fires from the look-alikes. Sensors cover a distance of 100 meters, so to be more effective, their placement has to be smart and risk-based. Although connectivity can be attained in remote forests with a mesh network, it is still challenging to maintain strong end-to-end communications and uptime at scale.
Dryad’s next steps involve its expansion with tools for fuel-moisture risk, besides detection, as well as stem-flow monitoring and tree growth. A new drone system will also be available to respond to wildfire alerts so there is timely extinguishing.
Predictions from two of the largest meteorological agencies forecast that global temperatures will reach record highs over the next five years, with increases exceeding 1.5 degrees leading to catastrophic weather phenomena for our planet. Artificial Intelligence has catalyzed a revolt in meteorology, offering more accurate predictions when traditional models once required massive supercomputers with useful insights still unavailable.
The Nvidia Earth 2 platform has stepped in to solve such problems in climate prediction, providing experts with more details in understanding and addressing climate change.
The Nvidia Earth 2 works as a complete cloud platform that offers AI-augmented, high-resolution climate and weather solutions. By combining the power of AI, physical simulations, and powerful graphic technologies, it can make global climate and weather predictions with accuracy and speed. The digital twin cloud platform basically develops an exact copy of Earth and runs ongoing.
The main AI technologies that it deploys are a generative AI foundation model that simulates global climate at kilometer resolution (cBottle), a diffusion model that generates results 500x faster and uses 10,000x less energy than usual methods (CorrDiff), and an AI weather prediction model that runs up to 5 orders of magnitude faster than standard numerical simulation (FourCastNet).
Nvidia’s Earth-2 cutting-edge technology is altering how scientists and professionals respond to climate resilience. Predicting extreme weather patterns at a kilometer scale was not an effortless task in the past, costing human lives and economic losses. The project’s innovation in providing faster predictions about upcoming weather events is an excellent opportunity for organizations. They can implement improved adaptation strategies and warning systems and enhance their overall preparedness.
Organizations such as the Weather Company have deployed Earth 2, to support it in creating detailed simulations for their weather services. Taiwan’s Central Weather Administration has also been among the organizations to use its diffusion models to enable typhoon predictions and evacuation plans, due to the high frequency of this phenomenon in the area.
Nvidia’s Earth 2 was officially launched in 2024, which means it still explores areas for further improvement. It accelerated the detailed simulation in an efficient way compared to the much slower performance of traditional models, yet there is a remaining distance that has to be covered for the maturing of the tool. Discussing AI Climate predictions against physical models necessitates a rigorous period of trial and error.
The platform is committed to expanding its capabilities, with the goal of being able to study more complicated climate patterns in the future. As part of its bigger goals to build better models, it has teamed up with the Max-Planck-Institute for Meteorology and the Allen Institute for AI.
Climate resilience is linked with proper waste management, but many disregard how important its role can be. For example, if a city does not have a functioning system that blocks waste and the waste clogs the drains, in case of heavy rainfall, serious floods will occur. That indicates waste management systems are not working well and are not designed for climate resilience.
Greyparrot has elevated the process so that it exploits artificial intelligence in the most effective way.
source: Greyparrot
Greyparrot, based in the UK, is a start-up founded to minimize how waste affects the environment by using what they call “waste intelligence.” Inspired by the African bird that mimics human voices, Greyparrot’s vision is to change the global waste management landscape and help people recover and redesign materials that would otherwise end up in landfills, all while reducing CO₂ emissions in the process.
Its waste intelligence platform includes Greyparrot Analyzer and Greyparrot Sync (API). These tools share insights for more than 111 waste categories across several key data layers. Among the data layers are the financial value, GHG emissions calculation, and brand. Their Analyzer units are installed over conveyor belts in material and plastics recovery facilities. Professionals in recycling services and FMCG brands can make smarter decisions on how to improve their recycling processes as well as comply with regulations.
Greyparrot is one more project that recognizes the potential of artificial intelligence and its role in fighting climate change. Deploying smart waste management that reduces GHG emissions is a prime example of how companies can contribute to ai climate resilience.
More than 50 waste facilities across 20+ countries are receiving results from using Greyparrot’s systems, such as how much the materials they lose are worth in value and what kind of materials can actually be recovered and not thrown away. These examples demonstrate how facilities can extract value from waste streams and contribute positively to climate resilience.
Waste management is a complicated process in itself, let alone when climate change and the continuous increase of waste materials and their specificity are involved. Using AI in waste management operations requires constant updates on technological possibilities. Skilled professionals and specialists need to understand and handle the mass collection of data and its analysis so there is enough progress in this area.
Greyparrot is expanding its technology, aiming to raise the number of automated sorting sites and enhance its waste intelligence to serve more companies throughout the ecosystems, changing the way companies design recycling products. By digitizing the waste value chain, Greyparrot takes quicker steps in the transition to a more circular economy.
Artificial intelligence can solve some of the greatest environmental problems. Innovative projects such as Google’s flood forecasting system and Dryad’s wildfire detection network explain how technology can work together with human skills to protect communities and the economy by making early predictions. Different fields are now applying AI, such as waste management with Greyparrot and biodiversity monitoring with Wildbook. These projects demonstrate how creative solutions can be activated while using climate resilience technology and offering access to a broader audience of professionals and experts. However, we must recognize that there are still roadblocks to overcome. For example, limitation of data, resource restrictions, or relevant knowledge can affect the progress.
Ongoing and relevant training can inform professionals about AI climate resilience strategies and how they can practically transfer the knowledge to their projects. The Sustainability Intelligence course by EcoSkills presents real-world models where executives can learn global patterns while meeting local needs.
