
In today’s business landscape, it is rare to find competitive and relevant organizations that don’t include sustainability as a key component of their strategy, demonstrating how significant it is.
When talking about sustainability, we refer to three areas: the environment, society, and the business’ profit. Sustainability is used as a synonym for ESG, a well-known acronym for Environmental, Social and Governance.
According to the World Economic Forum, 90% of executives believe sustainability is essential because organizations with a sustainability strategy can make long-term investments. Nowadays, an increasing number of organizations implement sustainability strategies. Thus, it’s evident that being a sustainable business is no longer optional but paramount.
In a world facing unprecedented challenges, the role of sustainability strategies has evolved into a crucial element of corporate planning and business models. Translating these strategies into tangible actions across all parts of the business is imperative. BETTER FUTURE FACTORY emphasizes that sustainability is not simply a trend but a vital part of a business strategy. A sustainable business approach integrates economic, environmental, and social dimensions into the fundamental operations of an organization. Key elements include Environmental Responsibility, Social Commitment, and Governance Requirements.
As KAIZEN mentions, a sustainability strategy takes into account the way the company’s activities affect issues like climate change, natural resource use, human rights, diversity and inclusion, business ethics, and transparency. A successful sustainability strategy mitigates risks, creates opportunities for innovation, growth, talent attraction, and retention, and improves reputation and brand value. To ensure its effectiveness, sustainability must be embedded in the company’s culture, from top management to every operational level.
Here are some of the main factors compelling organizations to embrace and prioritize sustainability:
Environmental and social practices significantly impact the long-term success of businesses. Some businesses outperform others in this area, giving them a competitive advantage. Sustainable business development is crucial for long-term success, and the following strategies can aid companies to do that.
Sustainable manufacturing, also known as green manufacturing or eco-friendly manufacturing.
Sustainable manufacturing means producing goods in an environmentally responsible and resource-efficient manner, according to Ignitec. By implementing sustainable design principles from the initial stages, companies can have numerous benefits, like less negative environmental impact, cost savings, resource efficiency, competitive advantage, and consumer choice. Thoughtful/ sustainable design and development of products can end up in products that live long and can be repaired easily. Using sustainable materials can guarantee that the design process closes loops and facilitates repair and reuse to promote a more circular economy. In addition, sustainable packaging prioritization aims for recyclable or compostable materials.
Implementation of LCA assessment
Life Cycle Analysis serves as a tool for assessing products’ environmental impact throughout their lifespan, from creation to disposal. Its objective is to identify and prioritize areas that contribute the most to the environmental footprint.
Resource efficiency maximization – implementation of circular economy principles (CE)
Minimizing waste, transforming waste into useful resources, and using renewable energy for production processes can contribute to high efficiency while closing loops to promote a circular economy. For instance, processes like sustainable manufacturing can reduce solid waste, which would otherwise have ended up in landfills. Significant decreases in raw material consumption and natural resource preservation are also spotted.
Improvement of energy efficiency
Energy efficiency is high among companies’ most important priorities. Via energy initiatives, businesses can lessen operational costs by diminishing dependence on electricity and fossil fuels. A company can be energy efficient by insulating the building, choosing LED lightbulbs, buying Energy Star-certified equipment, using a fuel-efficient fleet and organizing freight transportation, as VLS Environmental Solutions highlights.
Encourage remote work
Only some businesses can support remote work; nevertheless, many can transition to a somewhat hybrid workforce model. This transition can result in energy usage reduction. By encouraging remote work, the company’s electricity bill can be lower, as less is spent on lighting, climate management and plugged-in headquarters equipment. Thus, the environmental strain will be less. Employees would still use electricity while working remotely from home, although, in this case, their environmental impact would be more negligible. Additionally, employees who do not have to drive to work are not releasing GHG emissions, reducing, this way, fossil fuels and saving money.
Inequality reduction, ex. Gender inequalities
Nowadays, gender inequality remains a prominent social matter despite the improvements. According to AI Multiple, there are two common types of gender disparity in the workplace: gender pay discrepancy, which occurs when companies pay male employees more and provide better working conditions to male than female employees in the same position and occupational segregation, in which women are hired for non-technical jobs. At the same time, men hold most leadership roles.
Invest in employees well-being
BEYOND SAPIENS highlights that everything starts from each of us individually to deliver collective results. Research has shown that workers are more productive, engaged, and likely to stay in a company when they are content and healthy. Employee well-being is not merely about benefits. It is also about providing opportunities for professional development and career advancement, helping employees, this way, to feel more valued and fulfilled in their roles and helping the company retain top talent.
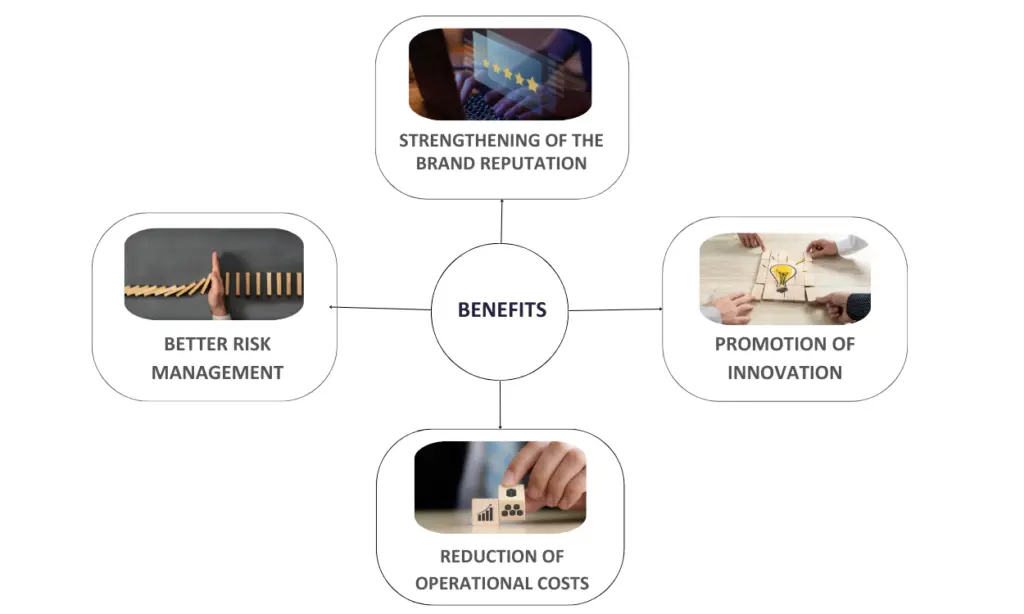
By placing focus on societal impact, environmental conscience, and employee well-being, a company establishes the foundation for long-term success.
Through proactive involvement in social causes and constructive contributions to communities, a corporation cultivates trust and loyalty among consumers who are progressively aligning their values with their purchasing choices. Moreover, adopting an environmentally conscious strategy not only reduces ecological damage but also promotes creativity, frequently resulting in financial savings and a competitive advantage.
Placing employee wellbeing as a top priority boosts morale, productivity, and retention rates, resulting in a motivated staff that fosters innovation and customer pleasure. In the long run, this holistic approach not only has positive effects on society and the environment, but also fosters a resilient and successful organization that can adjust and flourish in a constantly changing market.
